Celiac
Disease
 What Is Celiac Disease?
What Is Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is an immune reaction to eating gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye. If you have celiac disease, eating gluten triggers an immune response in your small intestine.
This reaction will damage your small intestine’s lining and prevents it from absorbing some nutrients (malabsorption). The intestinal damage often causes diarrhea, fatigue, weight loss, bloating and anemia, and can lead to serious complications.
There’s no cure for celiac disease, however, following a strict gluten-free diet can help manage symptoms and promote intestinal healing.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of celiac disease can vary greatly and differ in children and adults. Digestive signs and symptoms for adults include:
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating and gas
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Constipation
More than half the adults with celiac disease have signs and symptoms unrelated to the digestive system, including:
- Anemia, usually from iron deficiency
- Loss of bone density (osteoporosis) or softening of bone (osteomalacia)
- Itchy, blistery skin rash (dermatitis herpetiformis)
- Mouth ulcers
- Headaches and fatigue
- Nervous system injury, including numbness and tingling in the feet and hands, possible problems with balance, and cognitive impairment
- Joint pain
- Reduced functioning of the spleen (hyposplenism)
Children
Children with celiac disease are more likely than adults to have digestive problems, including:
- Chronic diarrhea
- Nausea and vomiting
- Swollen belly
- Constipation
- Gas
- Pale, foul-smelling stools
The inability to absorb nutrients might result in:
- Weight loss
- Damage to tooth enamel
- Failure to thrive for infants
- Anemia
- Irritability
- Short stature
- Delayed puberty
- Neurological symptoms, including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), learning disabilities, headaches, lack of muscle coordination and seizures
When To See A Doctor
If you have diarrhea or digestive discomfort that lasts for more than two weeks, consult your doctor. Consult your child’s doctor if your child is pale, irritable or failing to grow or has a potbelly and foul-smelling, bulky stools. Be sure to consult your doctor before trying a gluten-free diet. If you stop or even reduce the amount of gluten you eat before you’re tested for celiac disease, you can change the test results.
Celiac disease tends to run in families. If someone in your family has the condition, ask your doctor if you should be tested. Also ask your doctor about testing if you or someone in your family has a risk factor for celiac disease, such as type 1 diabetes.
Causes
Your genes combined with eating foods with gluten and other factors can contribute to celiac disease, but the precise cause isn’t known. Infant-feeding practices, gastrointestinal infections and gut bacteria might contribute, as well. Sometimes celiac disease becomes active after surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, viral infection or severe emotional stress.
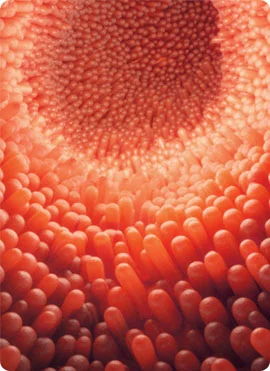
When the body’s immune system overreacts to gluten in food, the reaction damages the tiny, hairlike projections (villi) that line the small intestine. Villi absorb vitamins, minerals and other nutrients from the food you eat. If your villi are damaged, you can’t get enough nutrients, no matter how much you eat.
Risk Factors
Celiac disease tends to be more common in people who have:
- A family member with celiac disease or dermatitis herpetiformis
- Type 1 diabetes
- Down syndrome or Turner syndrome
- Autoimmune thyroid disease
- Microscopic colitis (lymphocytic or collagenous colitis)
- Addison’s disease
Complications
Untreated, celiac disease can cause:
- Malnutrition. This occurs if your small intestine can’t absorb enough nutrients. Malnutrition can lead to anemia and weight loss. In children, malnutrition can cause slow growth and short stature.
- Bone weakening. Malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D can lead to a softening of the bone (osteomalacia or rickets) in children and a loss of bone density (osteopenia or osteoporosis) in adults.
- Infertility and miscarriage. Malabsorption of calcium and vitamin D can contribute to reproductive issues.
- Lactose intolerance. Damage to your small intestine might cause you abdominal pain and diarrhea after eating or drinking dairy products that contain lactose. Once your intestine has healed, you might be able to tolerate dairy products again.
- Cancer. People with celiac disease who don’t maintain a gluten-free diet have a greater risk of developing several forms of cancer, including intestinal lymphoma and small bowel cancer.
- Nervous system problems. Some people with celiac disease can develop problems such as seizures or a disease of the nerves to the hands and feet (peripheral neuropathy).
Nonresponsive Celiac Disease
Some people with celiac disease don’t respond to what they consider to be a gluten-free diet. Nonresponsive celiac disease is often due to contamination of the diet with gluten. Working with a dietitian can help you learn how to avoid all gluten.
People with nonresponsive celiac disease might have:
- Bacteria in the small intestine (bacterial overgrowth)
- Microscopic colitis
- Poor pancreas function (pancreatic insufficiency)
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Difficulty digesting sugar found in dairy products (lactose), table sugar (sucrose), or a type of sugar found in honey and fruits (fructose)
- Refractory celiac disease
